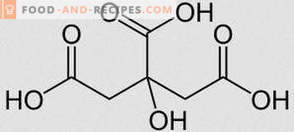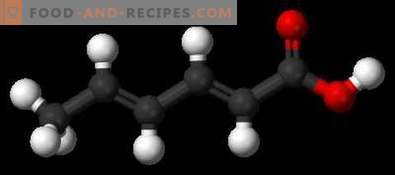
Sorbic acid is a colorless solid that is very poorly soluble in water, has no odor, but has a pronounced sour taste. When labeling food products, another acid name is commonly used - E200. Scientists are still arguing about whether to use this substance as a preservative. And is it really as safe as it seems at first glance.
What is useful sorbic acid?
E200 - a very powerful preservative, which has antibacterial properties. However, unlike other food additives, sorbic acid does not destroy microorganisms, but only slows down the process of their reproduction. Therefore, food products that contain this substance are not sterile. Moreover, they contain various groups of bacteria, including those that have a very beneficial effect on the human body. However, due to the fact that their process of development and reproduction is inhibited due to the presence of E200, food products retain their freshness and excellent quality much longer, do not grow moldy and do not rot.
Sorbic acid itself in small doses has a very positive effect on the human body, helping to strengthen the immune system and remove toxins from it. However, its antibacterial properties are manifested only in an environment with low acidity, therefore, when ingested into the human stomach, the preservative E200 is usually neutralized, after which it is eliminated from the body naturally.
Where is sorbic acid used?
The scope of E200 preservative is very wide. Initially, this substance obtained by distilling rowan juice in the middle of the 19th century was used as an additive to various drugs. However, it soon became clear that sorbic acid is good only when applied externally. From the mid-20th century, E200 is synthesized from ketene and crotonic aldehyde in industrial quantities and is used as a preservative.
Today, sorbic acid is added to dozens of different food products, including mayonnaise, sauces, all kinds of canned food, chocolate, soft drinks, pastries, jams and ready-to-cook foods. E200 is also used in the production of hard cheeses, sausages, ravioli, dumplings, wine and confectionery. According to existing standards, the permissible rate of the substance per 100 kg of the finished product should not exceed 250 g. However, in order to extend their shelf life, these requirements are often violated, with the result that a regular bun can retain its freshness for up to 20 days, without growing stale or molding. The same applies to various juices and compotes, which do not turn sour for a long time after opening the package, even if they are not stored in the refrigerator.
Sorbic acid damage
Scientifically it was found out that the permissible rate of E200 in the human body is no more than 25 mg per 1 kg of body weight. Therefore, poisoning with sorbic acid is mono only in those cases, if taken in pure form. After all, E200 is quite easily eliminated from the body naturally and does not have the ability to accumulate in tissues. It is proved that the preservative E200 does not possess carcinogenic properties, however, in people with increased sensitivity to acids, it can provoke a severe allergy, which manifests itself in the form of skin rashes and edema of tissues. However, it should be noted that today there are no more than 2 dozen such cases recorded worldwide.
It is much more dangerous that sorbic acid, when ingested by a human being , actively destroys vitamin B12, which is involved in many important processes. Therefore, people who abuse products with a high content of E200 preservative often suffer from nervous disorders, they have recorded an intense death of nerve cells. Research on the properties of sorbic acid and its effects on humans is still being studied, but on the basis of preliminary results, Australia has already decided to abandon this dietary supplement. In all other countries of the world, including Russia, E200 is allowed for use in the food and pharmaceutical industries.